Introduction
The blog post Artificial Intelligence Capabilities written in Nov’18 discusses the significance and capabilities of AI in the modern business world. It emphasises that AI’s real business value is often overshadowed by hype, unrealistic expectations, and concerns about machine control.
The post clarifies AI’s objectives and capabilities, defining AI simply as using computers to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. It outlines AI’s three main goals: capturing information, determining what is happening, and understanding why it is happening. I used an example of a lion chase to illustrate how humans and machines process information differently, highlighting that machines, despite their advancements, still struggle with understanding context as humans do (causality).
Additionally, it lists eight AI capabilities in use at the time: Image Recognition, Speech Recognition, Data Search, Data Patterns, Language Understanding, Thought/Decision Process, Prediction, and Understanding.
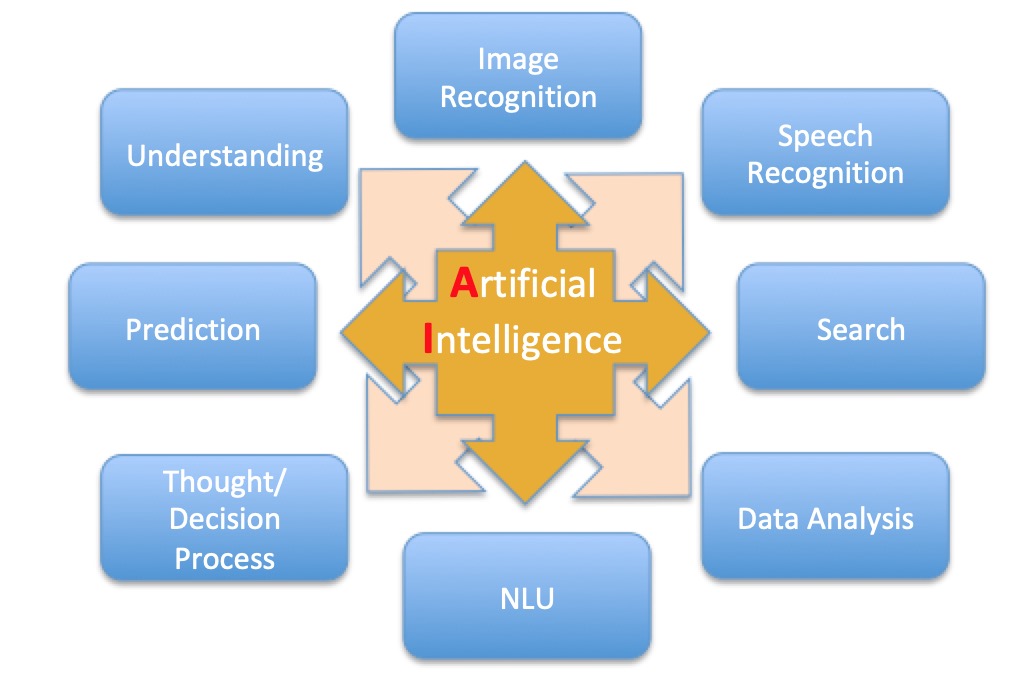
Each capability, like Image Recognition and Speech Recognition, is explained in terms of its function and technological requirements. The post emphasises that while machines have made significant progress, they still have limitations compared to human reasoning and understanding.
The landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities has evolved significantly since that earlier focus on objectives like capturing information, determining events, and understanding causality. In 2023, AI has reached impressive technical capabilities and has become deeply integrated into various aspects of everyday life and business operations.
2023 AI technical capabilities and daily use examples
Generative AI’s Breakout: AI in 2023 has been marked by the explosive growth of generative AI tools. Companies like OpenAI have revolutionised how businesses approach tasks that traditionally required human creativity and intelligence. Advanced models like GPT-4 and DALL-E 2, which have demonstrated remarkable humanlike outputs, significantly impacting the way businesses operate in the generation of unique content, design graphics, or even code software more efficiently, thereby reducing operational costs and enhancing productivity. For example, organisations are using generative AI in product and service development, risk and supply chain management, and other business functions. This shift has allowed companies to optimise product development cycles, enhance existing products, and create new AI-based products, leading to increased revenue and innovative business models.
AI in Data Management and Analytics: The use of AI in data management and analytics has revolutionised the way businesses approach data-driven decision-making. AI algorithms and machine learning models are adept at processing large volumes of data rapidly, identifying patterns and insights that would be challenging for humans to discern. These technologies enable predictive analytics, where AI models can forecast trends and outcomes based on historical data. In customer analytics, AI is used to segment customers, predict buying behaviours, and personalise marketing efforts. Financial institutions leverage AI in risk assessment and fraud detection, analysing transaction patterns to identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities. In healthcare, AI-driven data analytics assists in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and optimizing treatment plans. In the realm of supply chain and logistics, AI algorithms forecast demand, optimise inventory levels, and improve delivery routes. The integration of AI with big data technologies also enhances real-time analytics, allowing businesses to respond swiftly to changing market dynamics. Moreover, AI contributes to the democratisation of data analytics by providing tools that require less technical expertise. Platforms like Microsoft Fabric and Power BI, integrate AI (Microsoft Copilot) to enable users to generate insights through natural language queries, making data analytics more accessible across organizational levels. Microsoft Fabric, with its integration of Azure AI, represents a significant advancement in the realm of AI and analytics. This innovative platform, as of 2023, offers a unified solution for enterprises, covering a range of functions from data movement to data warehousing, data science, real-time analytics, and business intelligence. The integration with Azure AI services, especially the Azure OpenAI Service, enables the deployment of powerful language models, which facilitates a variety of AI applications such as data cleansing, content generation, summarisation, and natural language to code translation, auto-completion and quality assurance. Overall, AI in data management covering data engineering, analytics and science not only improves efficiency and accuracy but also drives innovation and strategic planning in various industries.
Regulatory Developments: The AI industry is experiencing increased regulation. For example, the U.S. has introduced guidelines to protect personal data and limit surveillance, and the EU is working on the AI Act, potentially the world’s first broad standard for AI regulation. These developments are likely to make AI systems more transparent, with an emphasis on disclosing data usage, limitations, and biases.
AI in Recruitment and Equality: AI is increasingly being used in recruitment processes. LinkedIn, a leader in professional networking and recruitment, has been utilising AI to enhance their recruitment processes. AI algorithms help filter through vast numbers of applications to identify the most suitable candidates. However, there’s a growing concern about potential discrimination, as AI systems can inherit biases from their training data, leading to a push for more impartial data sets and algorithms. The UK’s Equality Act 2010 and the General Data Protection Regulation in Europe regulate such automated decision-making, emphasising the importance of unbiased and fair AI use in recruitment. Moreover, LinkedIn has been working on AI systems that aim to minimise bias in recruitment, ensuring a more equitable and diverse hiring process.
AI in Healthcare: AI’s application in healthcare is growing rapidly. It ranges from analysing patient records to aiding in drug discovery and patient monitoring through to the resource demand and supply management of healthcare professionals. The global market for AI in healthcare, valued at approximately $11 billion in 2021, is expected to rise significantly. This includes using AI for real-time data acquisition from patient health records and in medical robotics, underscoring the need for safeguards to protect sensitive data. Companies like Google Health and IBM Watson Heath are utilizing AI to revolutionise healthcare with AI algorithms being used to analyse medical images for diagnostics, predict patient outcomes, and assist in drug discovery. Google’s AI system for diabetic retinopathy screening has shown to be effective in identifying patients at risk, thereby aiding in early intervention and treatment.
AI for Face Recognition: AI-powered face recognition technology is widely used, from banking apps to public surveillance. Face recognition technology is widely used in various applications, from unlocking smartphones to enhancing security systems. Apple’s Face ID technology, used in iPhones and iPads, is an example of AI-powered face recognition providing both convenience and security to users. Similarly, banks and financial institutions are using face recognition for secure customer authentication in mobile banking applications. However, this has raised concerns about privacy and fundamental rights. The EU’s forthcoming AI Act is expected to regulate such technologies, highlighting the importance of responsible and ethical AI usage.
AI’s Role in Scientific Progress: AI models like PaLM and Nvidia’s reinforcement learning agents have been used to accelerate scientific developments, from controlling hydrogen fusion to improving chip designs. This showcases AI’s potential to not only aid in commercial ventures but also to contribute significantly to scientific and technological advancements. AI’s impact on scientific progress can be seen in projects like AlphaFold by DeepMind (a subsidiary of Alphabet, Google’s parent company). AlphaFold’s AI-driven predictions of protein structures have significant implications for drug discovery and understanding diseases at a molecular level, potentially revolutionising medical research.
AI in Retail and E-commerce: Amazon’s use of AI in its recommendation system exemplifies how AI can drive sales and improve customer experience. The system analyses customer data to provide personalized product recommendations, significantly enhancing the shopping experience and increasing sales.
AI’s ambition of causality – the 3rd AI goal
AI’s ambition to evolve towards understanding and establishing causality represents a significant leap beyond its current capabilities in pattern recognition and prediction. Causality, unlike mere correlation, involves understanding the underlying reasons why events occur, which is a complex challenge for AI. This ambition stems from the need to make more informed and reliable decisions based on AI analyses.
For instance, in healthcare, an AI that understands causality could distinguish between factors that contribute to a disease and those that are merely associated with it. This would lead to more effective treatments and preventative strategies. In business and economics, AI capable of causal inference could revolutionise decision-making processes by accurately predicting the outcomes of various strategies, taking into account complex, interdependent factors. This would allow companies to make more strategic and effective decisions.
The journey towards AI understanding causality involves developing algorithms that can not only process vast amounts of data but also recognise and interpret the intricate web of cause-and-effect relationships within that data. This is a significant challenge because it requires the AI to have a more nuanced understanding of the world, akin to human-like reasoning. The development of such AI would mark a significant milestone in the field, bridging the gap between artificial intelligence and human-like intelligence – then it will know why the lion is chasing and why the human is running away – achieving the third AI goal.
In conclusion
AI in 2023 is not only more advanced but also more embedded in various sectors than ever before. Its rapid development brings both significant opportunities and challenges. The examples highlight the diverse applications of AI across different industries, demonstrating its potential to drive innovation, optimise operations, and create value in various business contexts.
For organisations, leveraging AI means balancing innovation with responsible use, ensuring ethical standards, and staying ahead in a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape. The potential for AI to transform industries, drive growth, and contribute to scientific progress is immense, but it requires a careful and informed approach to harness these benefits effectively.
The development of AI capable of understanding causality represents a significant milestone, as it would enable AI to have a nuanced, human-like understanding of complex cause-and-effect relationships, fundamentally enhancing its decision-making capabilities.
Looking forward to see where this technology will be in 2028…?

