Introduction: The Importance of Data Cataloguing in Modern Business
With big data now mainstream, managing vast amounts of information has become a critical challenge for businesses across the globe. Effective data management transcends mere data storage, focusing equally on accessibility and governability. “Data cataloguing is critical because it not only organizes data but also makes it accessible and actionable,” notes Susan White, a renowned data management strategist. This process is a vital component of any robust data management strategy.
Today, we’ll explore the necessary steps to establish a successful data catalogue. We’ll also highlight some industry-leading tools that can help streamline this complex process. “A well-implemented data catalogue is the backbone of data-driven decision-making,” adds Dr. Raj Singh, an expert in data analytics. “It provides the transparency needed for businesses to effectively use their data, ensuring compliance and enhancing operational efficiency.”
By integrating these expert perspectives, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of how data cataloguing can significantly benefit your organization, supporting more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Understanding Data Cataloguing
Data cataloguing involves creating a central repository that organises, manages, and maintains an organisation’s data to make it easily discoverable and usable. It not only enhances data accessibility but also supports compliance and governance, making it an indispensable tool for businesses.
Step-by-Step Guide to Data Cataloguing
1. Define Objectives and Scope
Firstly, identify what you aim to achieve with your data catalogue. Goals may include compliance, improved data discovery, or better data governance. Decide on the scope – whether it’s for the entire enterprise or specific departments.
2. Gather Stakeholder Requirements
Involve stakeholders such as data scientists, IT professionals, and business analysts early in the process. Understanding their needs – from search capabilities to data lineage – is crucial for designing a functional catalogue.
3. Choose the Right Tools
Selecting the right tools is critical for effective data cataloguing. Consider platforms like Azure Purview, which offers extensive metadata management and governance capabilities within the Microsoft ecosystem. For those embedded in the Google Cloud Platform, Google Cloud Data Catalog provides powerful search functionalities and automated schema management. Meanwhile, AWS Glue Data Catalog is a great choice for AWS users, offering seamless integration with other AWS services. More detail on tooling below.
4. Develop a Data Governance Framework
Set clear policies on who can access and modify the catalogue. Standardise how metadata is collected, stored, and updated to ensure consistency and reliability.
5. Collect and Integrate Data
Document all data sources and use automation tools to extract metadata. This step reduces manual errors and saves significant time.
6. Implement Metadata Management
Decide on the types of metadata to catalogue (technical, business, operational) and ensure consistency in its description and format.
- Business Metadata: This type of metadata provides context to data by defining commonly used terms in a way that is independent of technical implementation. The Data Management Body of Knowledge (DMBoK) notes that business metadata primarily focuses on the nature and condition of the data, incorporating elements related to Data Governance.
- Technical Metadata: This metadata supplies computer systems with the necessary information about data’s format and structure. It includes details such as physical database tables, access restrictions, data models, backup procedures, mapping specifications, data lineage, and more.
- Operational Metadata: As defined by the DMBoK, operational metadata pertains to the specifics of data processing and access. This includes information such as job execution logs, data sharing policies, error logs, audit trails, maintenance plans for multiple versions, archiving practices, and retention policies.
7. Populate the Catalogue
Use automated tools (see section on tooling below) and manual processes to populate the catalogue. Regularly verify the integrity of the data to ensure accuracy.
8. Enable Data Discovery and Access
A user-friendly interface is key to enhancing engagement and making data discovery intuitive. Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
9. Train Users
Provide comprehensive training and create detailed documentation to help users effectively utilise the catalogue.
10. Monitor and Maintain
Keep the catalogue updated with regular reviews and revisions. Establish a feedback loop to continuously improve functionality based on user input.
11. Evaluate and Iterate
Use metrics to assess the impact of the catalogue and make necessary adjustments to meet evolving business needs.
Data Catalogue’s Value Proposition
Data catalogues are critical assets in modern data management, helping businesses harness the full potential of their data. Here are several real-life examples illustrating how data catalogues deliver value to businesses across various industries:
- Financial Services: Improved Compliance and Risk Management – A major bank implemented a data catalogue to manage its vast data landscape, which includes data spread across different systems and geographies. The data catalogue enabled the bank to enhance its data governance practices, ensuring compliance with global financial regulations such as GDPR and SOX. By providing a clear view of where and how data is stored and used, the bank was able to effectively manage risks and respond to regulatory inquiries quickly, thus avoiding potential fines and reputational damage.
- Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care through Data Accessibility – A large healthcare provider used a data catalogue to centralise metadata from various sources, including electronic health records (EHR), clinical trials, and patient feedback systems. This centralisation allowed healthcare professionals to access and correlate data more efficiently, leading to better patient outcomes. For instance, by analysing a unified view of patient data, researchers were able to identify patterns that led to faster diagnoses and more personalised treatment plans.
- Retail: Personalisation and Customer Experience Enhancement – A global retail chain implemented a data catalogue to better manage and analyse customer data collected from online and in-store interactions. With a better-organised data environment, the retailer was able to deploy advanced analytics to understand customer preferences and shopping behaviour. This insight enabled the retailer to offer personalised shopping experiences, targeted marketing campaigns, and optimised inventory management, resulting in increased sales and customer satisfaction.
- Telecommunications: Network Optimisation and Fraud Detection – A telecommunications company utilised a data catalogue to manage data from network traffic, customer service interactions, and billing systems. This comprehensive metadata management facilitated advanced analytics applications for network optimisation and fraud detection. Network engineers were able to predict and mitigate network outages before they affected customers, while the fraud detection teams used insights from integrated data sources to identify and prevent billing fraud effectively.
- Manufacturing: Streamlining Operations and Predictive Maintenance – In the manufacturing sector, a data catalogue was instrumental for a company specialising in high-precision equipment. The catalogue helped integrate data from production line sensors, machine logs, and quality control to create a unified view of the manufacturing process. This integration enabled predictive maintenance strategies that reduced downtime by identifying potential machine failures before they occurred. Additionally, the insights gained from the data helped streamline operations, improve product quality, and reduce waste.
These examples highlight how a well-implemented data catalogue can transform data into a strategic asset, enabling more informed decision-making, enhancing operational efficiencies, and creating a competitive advantage in various industry sectors.
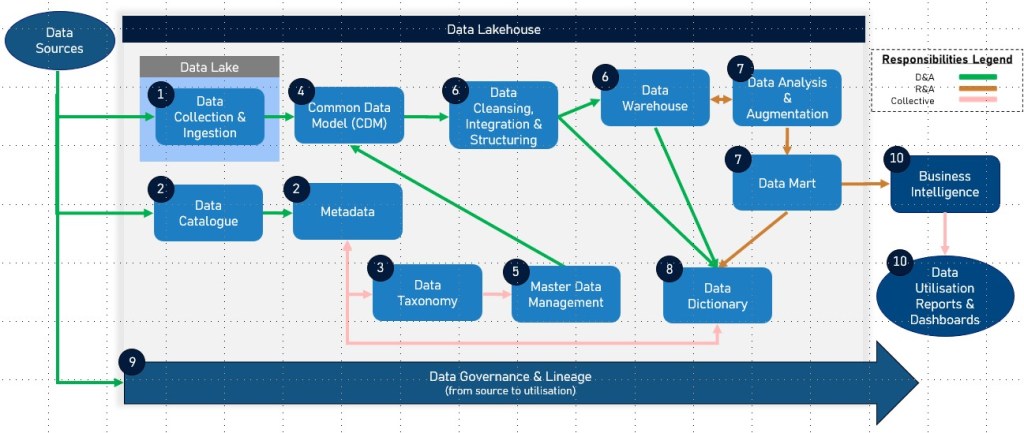
A data catalog is an organized inventory of data assets in an organization, designed to help data professionals and business users find and understand data. It serves as a critical component of modern data management and governance frameworks, facilitating better data accessibility, quality, and understanding. Below, we discuss the key components of a data catalog and provide examples of the types of information and features that are typically included.
Key Components of a Data Catalog
- Metadata Repository
- Description: The core of a data catalog, containing detailed information about various data assets.
- Examples: Metadata could include the names, types, and descriptions of datasets, data schemas, tables, and fields. It might also contain tags, annotations, and extended properties like data type, length, and nullable status.
- Data Dictionary
- Description: A descriptive list of all data items in the catalog, providing context for each item.
- Examples: For each data element, the dictionary would provide a clear definition, source of origin, usage guidelines, and information about data sensitivity and ownership.
- Data Lineage
- Description: Visualization or documentation that explains where data comes from, how it moves through systems, and how it is transformed.
- Examples: Lineage might include diagrams showing data flow from one system to another, transformations applied during data processing, and dependencies between datasets.
- Search and Discovery Tools
- Description: Mechanisms that allow users to easily search for and find data across the organization.
- Examples: Search capabilities might include keyword search, faceted search (filtering based on specific attributes), and full-text search across metadata descriptions.
- User Interface
- Description: The front-end application through which users interact with the data catalog.
- Examples: A web-based interface that provides a user-friendly dashboard to browse, search, and manage data assets.
- Access and Security Controls
- Description: Features that manage who can view or edit data in the catalog.
- Examples: Role-based access controls that limit users to certain actions based on their roles, such as read-only access for some users and edit permissions for others.
- Integration Capabilities
- Description: The ability of the data catalog to integrate with other tools and systems in the data ecosystem.
- Examples: APIs that allow integration with data management tools, BI platforms, and data lakes, enabling automated metadata updates and interoperability.
- Quality Metrics
- Description: Measures and indicators related to the quality of data.
- Examples: Data quality scores, reports on data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness.
- Usage Tracking and Analytics
- Description: Tools to monitor how and by whom the data assets are accessed and used.
- Examples: Logs and analytics that track user queries, most accessed datasets, and patterns of data usage.
- Collaboration Tools
- Description: Features that facilitate collaboration among users of the data catalog.
- Examples: Commenting capabilities, user forums, and shared workflows that allow users to discuss data, share insights, and collaborate on data governance tasks.
- Organisational Framework and Structure
- The structure of an organisation itself is not typically a direct component of a data catalog. However, understanding and aligning the data catalog with the organizational structure is crucial for several reasons:
- Role-Based Access Control: The data catalog often needs to reflect the organizational hierarchy or roles to manage permissions effectively. This involves setting up access controls that align with job roles and responsibilities, ensuring that users have appropriate access to data assets based on their position within the organization.
- Data Stewardship and Ownership: The data catalog can include information about data stewards or owners who are typically assigned according to the organizational structure. These roles are responsible for the quality, integrity, and security of the data, and they often correspond to specific departments or business units.
- Customization and Relevance: The data catalog can be customized to meet the specific needs of different departments or teams within the organization. For instance, marketing data might be more accessible and prominently featured for the marketing department in the catalog, while financial data might be prioritized for the finance team.
- Collaboration and Communication: Understanding the organizational structure helps in designing the collaboration features of the data catalog. It can facilitate better communication and data sharing practices among different parts of the organization, promoting a more integrated approach to data management.
- In essence, while the organisational structure isn’t stored as a component in the data catalog, it profoundly influences how the data catalog is structured, accessed, and utilised. The effectiveness of a data catalog often depends on how well it is tailored and integrated into the organizational framework, helping ensure that the right people have the right access to the right data at the right time.
- The structure of an organisation itself is not typically a direct component of a data catalog. However, understanding and aligning the data catalog with the organizational structure is crucial for several reasons:
Example of a Data Catalog in Use
Imagine a large financial institution that uses a data catalog to manage its extensive data assets. The catalog includes:
- Metadata Repository: Contains information on thousands of datasets related to transactions, customer interactions, and compliance reports.
- Data Dictionary: Provides definitions and usage guidelines for key financial metrics and customer demographic indicators.
- Data Lineage: Shows the flow of transaction data through various security and compliance checks before it is used for reporting.
- Search and Discovery Tools: Enable analysts to find and utilize specific datasets for developing insights into customer behavior and market trends.
- Quality Metrics: Offer insights into the reliability of datasets used for critical financial forecasting.
By incorporating these components, the institution ensures that its data is well-managed, compliant with regulations, and effectively used to drive business decisions.
Tiveness of a data catalog often depends on how well it is tailored and integrated into the organisational framework, helping ensure that the right people have the right access to the right data at the right time.
Tooling
For organizations looking to implement data cataloging in cloud environments, the major cloud providers – Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Amazon Web Services (AWS) – each offer their own specialised tools.
Here’s a comparison table that summarises the key features, descriptions, and use cases of data cataloging tools offered by Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Amazon Web Services (AWS):
| Feature | Azure Purview | Google Cloud Data Catalog | AWS Glue Data Catalog |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | A unified data governance service that automates the discovery of data and cataloging. It helps manage and govern on-premise, multi-cloud, and SaaS data. | A fully managed and scalable metadata management service that enhances data discovery and understanding within Google Cloud. | A central repository that stores structural and operational metadata, integrating with other AWS services. |
| Key Features | – Automated data discovery and classification. – Data lineage for end-to-end data insight. – Integration with Azure services like Azure Data Lake, SQL Database, and Power BI. | – Metadata storage for Google Cloud and external data sources. – Advanced search functionality using Google Search technology. – Automatic schema management and discovery. | – Automatic schema discovery and generation. – Serverless design, scales with data. – Integration with AWS services like Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Redshift. |
| Use Case | Best for organizations deeply integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem, seeking comprehensive governance and compliance capabilities. | Ideal for businesses using multiple Google Cloud services, needing a simple, integrated approach to metadata management. | Suitable for AWS-centric environments that require a robust, scalable solution for ETL jobs and data querying. |
This table provides a quick overview to help you compare the offerings and decide which tool might be best suited for your organizational needs based on the environment you are most invested in.
Conclusion
Implementing a data catalogue can dramatically enhance an organisation’s ability to manage data efficiently. By following these steps and choosing the right tools, businesses can ensure their data assets are well-organised, easily accessible, and securely governed. Whether you’re part of a small team or a large enterprise, embracing these practices can lead to more informed decision-making and a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.