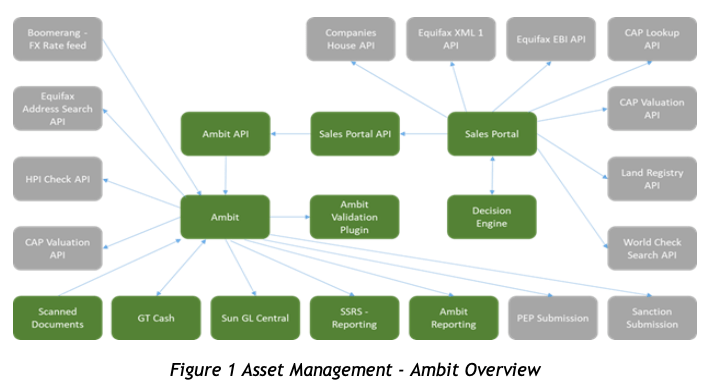
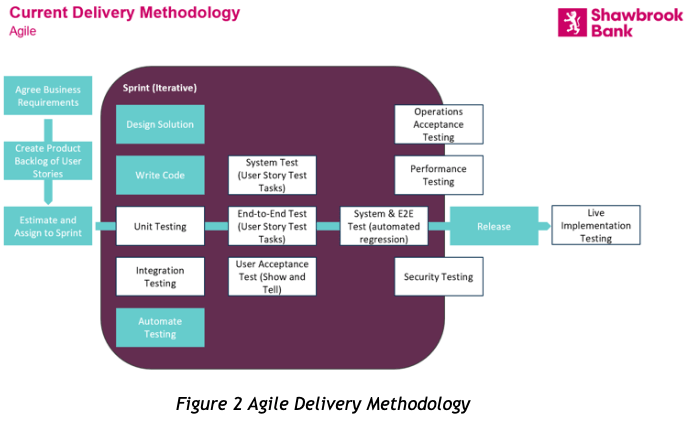
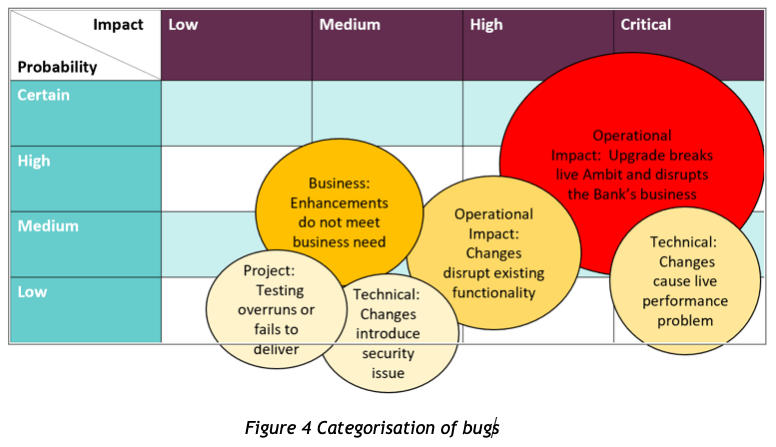
For businesses to stay relevant and ahead of the competition requires embracing cutting-edge technologies. One such transformative technology is generative AI. This blog post delves into how generative AI can revolutionise business operations, enhance creativity, and foster innovation. By establishing an AI Centre of Excellence, companies can effectively integrate AI into their workflows, empowering employees and driving efficiency. Whether you’re a large enterprise or a nimble start-up, this guide provides valuable insights into harnessing the power of generative AI to propel your business into the future. Join us as we explore the potential of AI and its impact on the modern workplace.
The Potential of Generative AI
Generative AI, when harnessed correctly, has the power to revolutionise the way companies operate, innovate, and compete. The key to unlocking this potential lies in establishing an AI Centre of Excellence (CoE) that integrates IT with learning and development to meet business needs.
Establishing an AI Centre of Excellence
An AI Centre of Excellence is not exclusive to large enterprises; even smaller companies can set one up. In fact, smaller businesses can be more agile and flexible, enabling them to outpace larger competitors in AI adoption. The CoE requires a two-pronged approach: learning from external best practices and understanding internal AI usage.
Learning from Generative AI Best Practices
Look Outward: The first step is to observe how other companies have successfully integrated AI into their operations. These companies serve as valuable case studies, showcasing both successes and challenges. For example, some companies use AI for creative content generation in marketing, while others apply it to predict customer behaviour in sales. By studying these practices, businesses can formulate a unified AI strategy.
Look Inward: The second step is an internal audit to understand how employees are currently using generative AI. This can reveal unexpected insights and areas for improvement. Encouraging employees to share their AI experiences fosters a culture of innovation and makes AI integration a company-wide effort.
Overcoming Integration Challenges
Many companies face challenges when integrating AI into their workflows. However, initial evidence suggests that AI can boost individual productivity by 20% to 70%, with output quality often surpassing non-AI-assisted tasks. This highlights AI’s potential as a personal productivity tool, especially when used by experts in their fields.
Despite this, AI currently enhances individual productivity more than organisational productivity. As noted by Ethan Mollick from the Wharton School, AI can be unpredictable and error-prone, making it difficult to scale across an organisation. However, recognising AI’s potential as a personal productivity tool and leveraging it within your organisation can empower employees and improve efficiency. As AI technology evolves, it will become more reliable and scalable, eventually enhancing overall organisational productivity.
Key Principles for a Successful AI Centre of Excellence
Once a company has gathered the necessary information, the next step is to establish an AI Centre of Excellence. This centre should be co-led by teams from IT and HR, combining technical expertise with a focus on learning and development. The CoE serves as a hub for AI-related activities, providing guidance, setting best practices, and ensuring alignment across departments.
To ensure success, the AI Centre of Excellence should adhere to the following guiding principles:
- Clear Vision and Mission: Define the strategic objectives of the CoE and align them with the overall business strategy. For example, if the goal is to leverage AI for content creation, the mission could be to develop and implement best practices in this area.
- Foster Collaboration and Communication: Act as a bridge between departments, facilitating the sharing of knowledge and best practices. For instance, insights from the marketing team’s use of AI can benefit other departments through the CoE.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine processes to remain effective and relevant. Stay updated with the latest AI technologies and incorporate them into the company’s practices.
- Promote a Culture of Learning and Development: Provide training and resources to enhance employees’ AI skills and knowledge. Offer workshops on using generative AI tools and resources for self-learning.
Serving Business Operations Through an AI Centre of Excellence
The ultimate goal of establishing an AI Centre of Excellence is to enhance business operations. Generative AI can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. By learning from others, understanding internal usage, and centralising AI initiatives, companies can harness AI’s potential and transform their operations.
The CoE plays a crucial role in this transformation, guiding the integration of AI into business operations. Whether it’s automating routine tasks, generating creative content, or predicting market trends, the CoE ensures these initiatives align with strategic objectives and best practices.
For example, to streamline customer service operations with AI, the CoE could develop a roadmap, identify the best AI tools, train staff, and set up a system for monitoring and improvement.
Moreover, the CoE fosters a culture of continuous learning and innovation, keeping the company up-to-date with AI advancements, encouraging exploration of new AI applications, and promoting experimentation and risk-taking.
Conclusion: GenAI – A Path to Growth and Success
The journey towards effective use of generative AI may seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can lead to unprecedented growth and success. Embrace the potential of AI, establish your Centre of Excellence, and watch as AI propels your business into the future.
Remember, the future of business lies in not just adopting new technologies, but understanding, integrating, and using them to drive operational excellence. Let the Centre of Excellence be your guide on this journey towards a future powered by generative AI.
Are you ready to unlock the full potential of generative AI and transform your business operations? At renierbotha Ltd, we specialise in helping companies of all sizes establish AI Centres of Excellence, ensuring seamless integration of AI technologies into your workflow. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing tailored solutions that drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and give you a competitive edge.
Get in touch with renierbotha Ltd today to start your journey towards a future powered by generative AI. Contact us directly to learn more about how we can support your AI initiatives and help your business thrive in the modern landscape.