Day 4 of Renier Botha’s 10-Day Blog Series on Navigating the Future: The Evolving Role of the CTO
For almost all modern companies, digital transformation is no longer a choice but a necessity. Modernizing IT infrastructure and driving innovation are crucial for organizations aiming to stay competitive and relevant. Leading successful digital transformation initiatives requires a strategic approach, a clear vision, and the ability to navigate complex changes. This comprehensive blog post will provide insights into effective digital transformation strategies that streamline operations and foster growth.
Understanding Digital Transformation
Digital transformation involves integrating digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how organizations operate and deliver value to customers. It encompasses a broad range of initiatives, including cloud computing, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and more.
Why Digital Transformation Matters
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automating processes and leveraging data analytics improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Improved Customer Experience: Personalized and seamless customer interactions drive satisfaction and loyalty.
- Innovation and Growth: New business models and revenue streams emerge from technological advancements.
- Competitive Advantage: Staying ahead of the competition requires continuous adaptation and innovation.
Key Components of Digital Transformation
Successful digital transformation initiatives typically involve several key components:
1. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. It enables organizations to access computing resources on-demand, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and software.
Example: Capital One has embraced cloud computing to modernize its IT infrastructure, resulting in improved agility and reduced costs. The bank migrated its applications to AWS, enabling faster deployment of new services and enhanced customer experiences.
2. Data Analytics and Big Data
Harnessing the power of data analytics and big data allows organizations to gain valuable insights, drive decision-making, and optimize operations. By analyzing large datasets, businesses can identify trends, predict customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions.
Example: Procter & Gamble uses data analytics to optimize its supply chain and improve product development. By analyzing data from various sources, P&G can predict demand, manage inventory, and reduce costs.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML technologies enable organizations to automate tasks, enhance customer interactions, and improve decision-making processes. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and provide actionable insights.
Example: Netflix leverages AI and ML to deliver personalized content recommendations to its users. By analyzing viewing habits and preferences, Netflix can suggest relevant content, increasing user engagement and satisfaction.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technologies connect devices and collect data, enabling organizations to monitor and manage assets in real-time. This connectivity enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports predictive maintenance.
Example: General Electric (GE) uses IoT to monitor and maintain its industrial equipment. The company’s Predix platform collects data from sensors embedded in machines, allowing GE to predict maintenance needs and reduce operational disruptions.
5. Digital Culture and Workforce
A successful digital transformation requires a cultural shift within the organization. Employees must embrace new technologies and adapt to changing workflows. Providing training and fostering a culture of innovation are essential for driving transformation.
Example: Microsoft transformed its corporate culture under CEO Satya Nadella, emphasizing collaboration, continuous learning, and a growth mindset. This cultural shift has been instrumental in Microsoft’s successful digital transformation.
Strategies for Leading Digital Transformation
Leading digital transformation initiatives involves strategic planning, effective execution, and continuous improvement. Here are some strategies for CTOs to consider:
1. Develop a Clear Vision and Strategy
A successful digital transformation starts with a clear vision and strategy. Define the objectives, goals, and desired outcomes of the transformation. Align the strategy with the organization’s overall business goals and ensure buy-in from all stakeholders.
2. Engage Leadership and Stakeholders
Leadership commitment is crucial for driving digital transformation. Engage senior leaders and stakeholders to champion the initiative and allocate necessary resources. Foster a collaborative environment where everyone understands the importance of transformation and their role in its success.
3. Focus on Customer Experience
Customer experience should be at the heart of digital transformation. Understand customer needs and preferences, and leverage technology to deliver personalized and seamless experiences. Collect feedback and continuously improve customer interactions.
4. Invest in Technology and Infrastructure
Invest in the right technologies and infrastructure to support digital transformation. This includes cloud computing, data analytics platforms, AI/ML tools, and IoT devices. Ensure that the infrastructure is scalable and secure to accommodate future growth.
5. Foster a Culture of Innovation
Encourage a culture of innovation by promoting experimentation, learning, and collaboration. Provide employees with the tools and training they need to embrace new technologies and processes. Recognize and reward innovative ideas and initiatives.
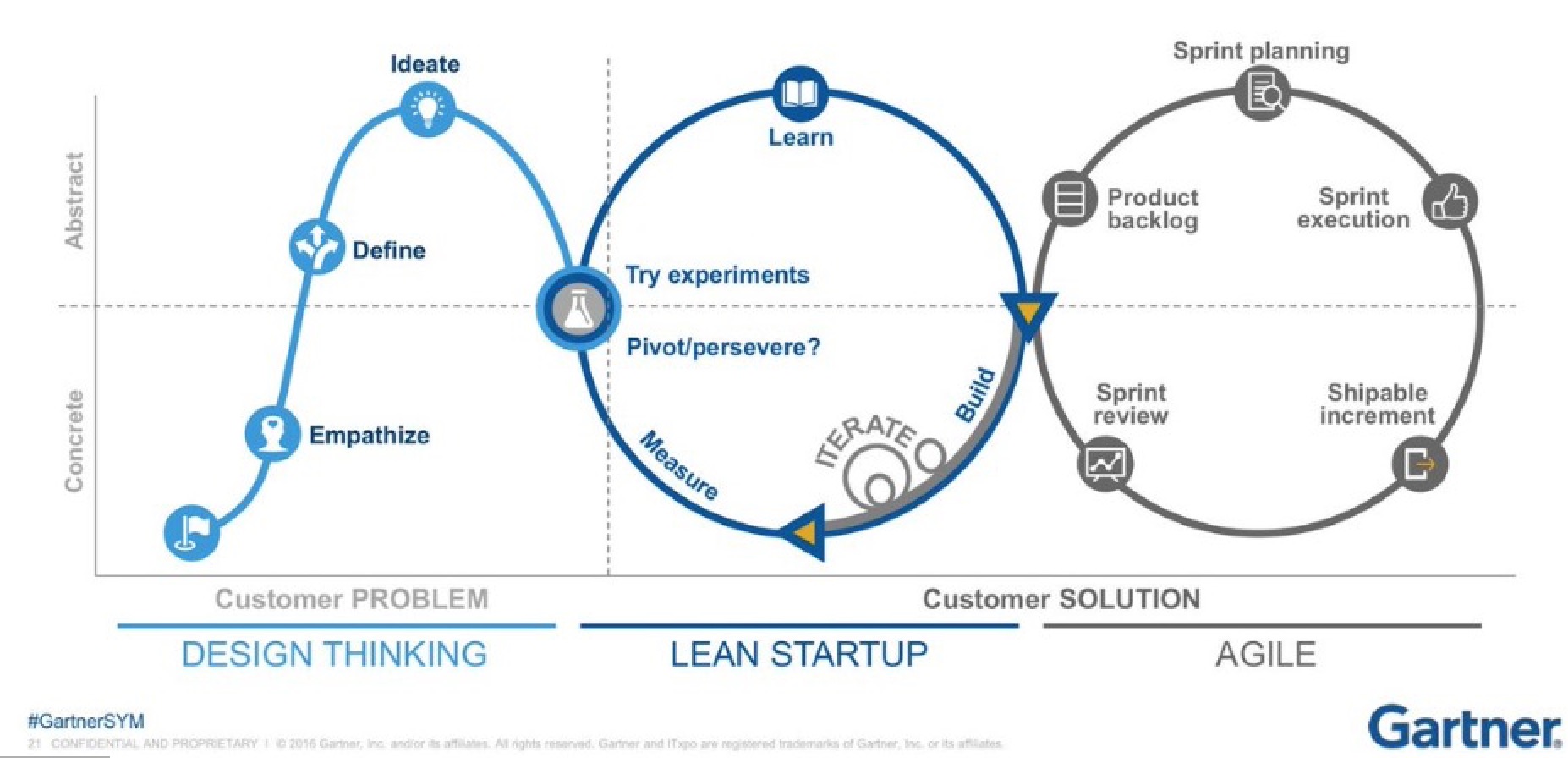
6. Implement Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies enable organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs. Adopt agile practices to streamline development processes, improve collaboration, and accelerate time-to-market for new products and services.
7. Monitor and Measure Progress
Regularly monitor and measure the progress of digital transformation initiatives. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track success and identify areas for improvement. Continuously refine strategies based on data-driven insights and feedback.
Real-World Examples of Digital Transformation
Example 1: Amazon
Amazon’s digital transformation journey has been characterized by continuous innovation and a customer-centric approach. The company has leveraged cloud computing, AI, and data analytics to revolutionize e-commerce and supply chain management. Amazon Web Services (AWS) has become a leading cloud platform, enabling businesses worldwide to transform their operations.
Example 2: Domino’s Pizza
Domino’s Pizza has embraced digital transformation to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. The company’s “AnyWare” platform allows customers to order pizza through various digital channels, including smartwatches, voice assistants, and social media. Domino’s has also implemented AI-powered chatbots and real-time order tracking to improve customer satisfaction.
Example 3: Siemens
Siemens has undergone a digital transformation to become a leader in industrial automation and smart manufacturing. The company’s MindSphere platform connects industrial equipment and collects data for analysis, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized production processes. Siemens’ digital initiatives have improved efficiency and reduced downtime in manufacturing operations.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is a critical driver of modernizing IT infrastructure and fostering innovation. By leveraging technologies such as cloud computing, data analytics, AI, ML, and IoT, organizations can streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. Leading successful digital transformation initiatives requires a clear vision, leadership commitment, a culture of innovation, and continuous monitoring and improvement.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, organizations must embrace digital transformation to remain competitive and relevant. By adopting strategic approaches and leveraging technological advancements, leaders can navigate the complexities of transformation and achieve lasting success.
Read more blog post on Digital Transformation here : https://renierbotha.com/tag/digital-transformation/
Stay tuned as we continue to explore critical topics in our 10-day blog series, “Navigating the Future: A 10-Day Blog Series on the Evolving Role of the CTO” by Renier Botha.
Visit www.renierbotha.com for more insights and expert advice.