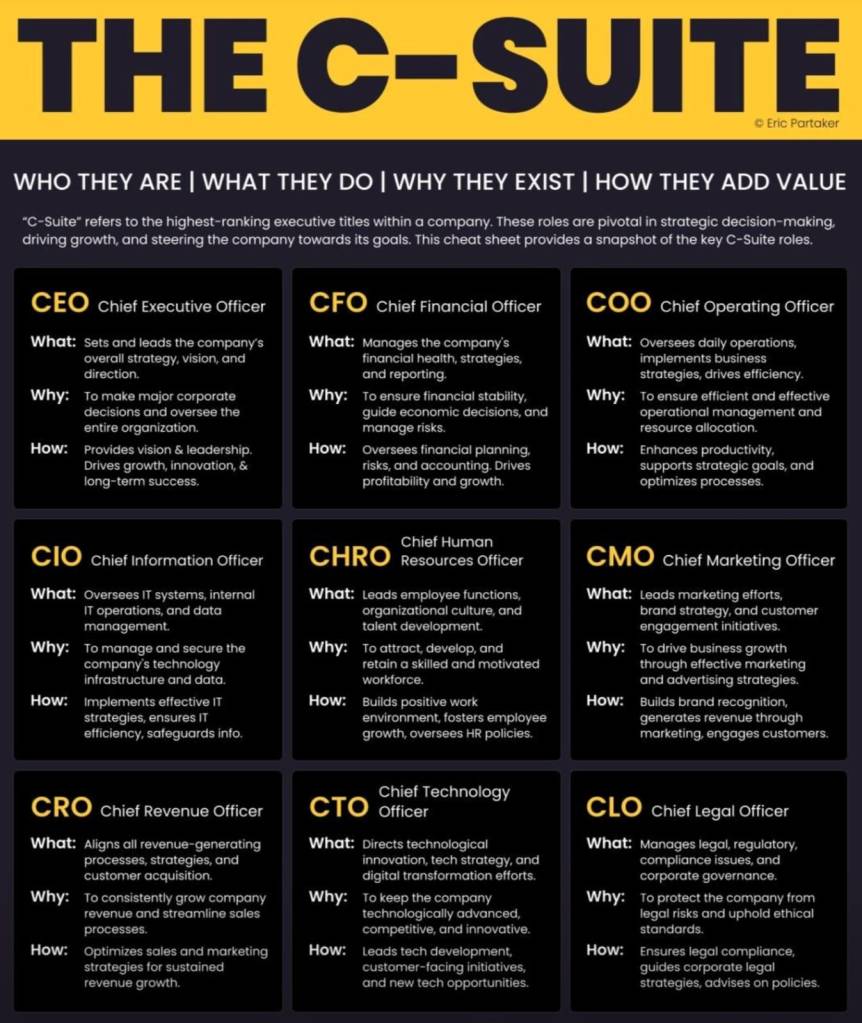
WHO they are, What the do, Why they exist, How they add value
In corporate leadership, the C-Suite stands as the command centre, where strategic decisions are made, and the future of the company is shaped. Comprising key executives with specialised roles, the C-Suite plays a crucial role in steering organisations towards success. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of the C-Suite, shedding light on the responsibilities and value each role brings to the table.
- CEO – Chief Executive Officer
The CEO, or Chief Executive Officer, is the captain of the ship, responsible for charting the company’s course and ensuring its overall success. The CEO sets the vision, mission, and strategy, providing leadership to the entire organisation. They are the ultimate decision-maker, accountable to the board of directors and stakeholders.
- CFO – Chief Financial Officer
The CFO, or Chief Financial Officer, is the financial maestro of the C-Suite. Tasked with overseeing the financial health of the organisation, the CFO manages budgets, financial planning, and investment strategies. They play a pivotal role in risk management, ensuring sustainable growth and profitability.
- COO – Chief Operating Officer
The COO, or Chief Operating Officer, is the executor of the CEO’s vision. Responsible for day-to-day operations, the COO ensures that the company’s processes and systems align with strategic goals. They focus on efficiency, productivity, and scalability, optimising internal functions for maximum performance.
- CIO – Chief Information Officer
In the digital age, the CIO, or Chief Information Officer, holds a critical role. Charged with managing the company’s technology infrastructure, the CIO ensures that information systems align with business objectives. They play a pivotal role in driving innovation and digital transformation.
- CHRO – Chief Human Resources Officer
The CHRO, or Chief Human Resources Officer, is the guardian of the company’s most valuable asset—its people. Responsible for talent acquisition, employee development, and creating a positive work culture, the CHRO plays a key role in shaping the organisation’s human capital strategy.
- CMO – Chief Marketing Officer
The CMO, or Chief Marketing Officer, is the storyteller-in-chief. Charged with building and promoting the company’s brand, the CMO develops marketing strategies to drive growth and customer engagement. They are instrumental in shaping the company’s public image and market positioning.
- CRO – Chief Revenue Officer
The CRO, or Chief Revenue Officer, is the architect of revenue streams. Focused on driving sales and revenue growth, the CRO collaborates with sales, marketing, and other departments to optimise customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- CTO – Chief Technology Officer
The CTO, or Chief Technology Officer, is the technology visionary. Tasked with leading technological innovation, the CTO develops and implements technology strategies that align with the company’s business goals. They often play a crucial role in product development and ensuring technological competitiveness.
- CLO – Chief Legal Officer
The CLO, or Chief Legal Officer, is the legal guardian of the organisation. Responsible for managing legal risks and ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, the CLO provides legal counsel to the executive team and oversees matters such as contracts, intellectual property, and litigation.
Summary – Cheat sheet
Conclusion
The C-Suite represents a powerhouse of expertise, each member contributing their unique skills to the overall success of the organisation. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of the CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, CHRO, CMO, CRO, CTO, and CLO, we gain insights into the intricate workings of corporate leadership. Together, these leaders form a cohesive unit, steering the ship through the complexities of the business world, adding significant value to the organisation and its stakeholders.



